Codominance

Refers to a relationship between two alleles of a gene.

Variation within a population in which a graded series of intermediate phenotypes falls between the extremes.
Dihybrid Cross
Is a cross between F1 offspring of two individuals that differ in two traits of particular interest.
Epistasis

Where the effects of one gene are modified by one or several other genes.
F1

The offspring of an initial genetic cross.
Gene

is a unit of heredity in a living organism.
Genotype

is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual.
Heterozygous

When cells of diploid organism contain two different alleles of a gene.
Homozygous Dominant

That it has two dominant alleles.
Homozygous Recessive

A same trait that is not the stronger trait which is dominant.
Hybrid Offspring

Offspring of crosses between parents with different traits.
Incomplete Dominance

Is a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely dominant over the other.
Independent Assorment
States that allele pairs separate independently during the formation of gametes.
Monohybrid Cross

Is a cross between two parents that breed true for different versions of a single trait.
Multiple Allele System
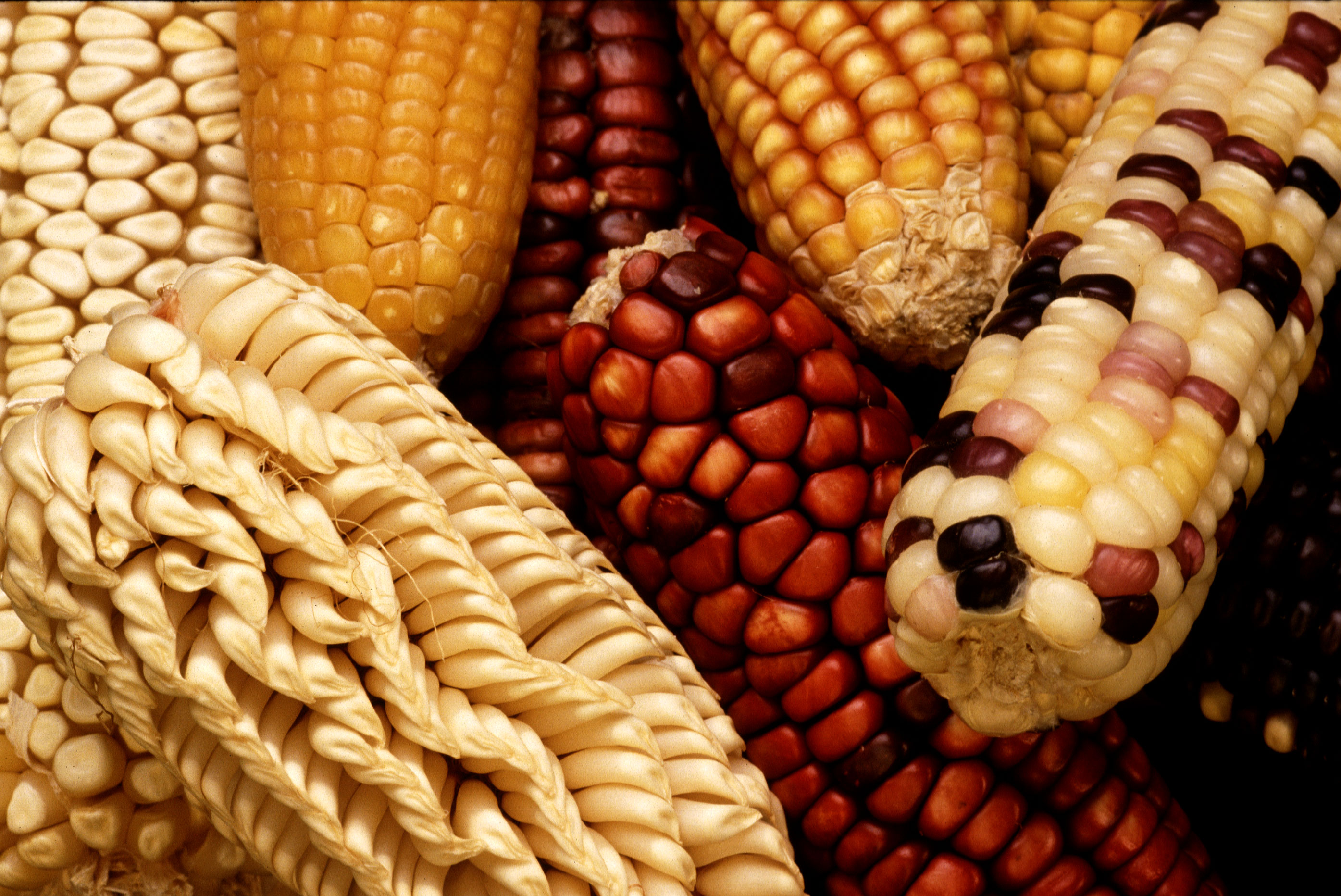

A "variation" of a gene.Genes which have more than two alleles.
Phenotype
Is any observable characteristic or trait of an organism.
Pleiotropy

Is the condition in which a gene influences the phenotype of more than one part of the body.
Probability

The chance that each outcome of a given event will occur is proportional to the number of ways the outcome can be reached.
Punnet-square Method
A way to predict probable outcomes of a genetic cross.
Segregation






te quierouuu
ReplyDeleteVery good!
ReplyDeletenice work
ReplyDelete